











































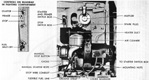

| T23: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | October 1943 | Total acceptances | 250 |
| Manufacturer | Detroit Tank Arsenal | Crew |
|
| T23: Dimensions | |||
| Combat weight | 75,311lbs 34,161kg |
Height over cupola | 98.8" 251cm |
| Length without gun, with sandshields | 236.9" 601.7cm |
Gun overhang forward | 60.6" 154cm |
| Width over sandshields | 122.5" 311.2cm |
Tread | 102" 259cm |
| Ground clearance | 19.1" 48.5cm |
Fire height | 77" 195cm |
| Turret ring diameter | 69" 175cm |
Ground pressure, zero penetration | 15.5psi 1.08kg/cm² |
| T23: Armament | |||||
| Type | Mount | Ammunition | Traverse | Max traverse rate | Elevation |
| 76mm Gun M1A1 | M62 in turret | 66 rounds | 360° (manual and hydraulic) |
24°/sec | +25° to -10° (manual) |
| .50cal M2HB MG | Flexible in turret AA mount | 300 rounds | 360° (manual) |
-- | Manual |
| .30cal M1919A4 MG | Coaxial to 76mm gun | 5,000 rounds | 360° (manual and hydraulic) |
24°/sec | +25° to -10° (manual) |
| .30cal M1919A4 MG | Ball mount D93884 in right bow | Manual | -- | Manual | |
| 2" Mortar M3 (smoke) | Fixed in turret roof | 12 rounds | 360° (manual and hydraulic) |
24°/sec | 35° (fixed) |
| Aiming equipment | |||||
| Periscope M4A1 with telescope M47; telescope M71D for gunner | |||||
| Stabilizer | |||||
| Elevation only | |||||
| T23: Armor | ||
| Assembly | ||
| Welding | ||
| Hull | ||
| Rolled and cast homogeneous steel | ||
| Location | Thickness | Angle from vertical |
| Upper front | 3.0" 7.6cm |
47° |
| Lower front | 2.5" 6.4cm |
56° |
| Front sides | 2.0" 5.1cm |
0° |
| Rear sides | 1.5" 3.8cm |
0° |
| Rear | 1.5" 3.8cm |
0° to 30° |
| Top | .75" 1.9cm |
90° |
| Front floor | 1.0" 2.5cm |
90° |
| Rear floor | .5" 1.3cm |
90° |
| Turret | ||
| Cast homogeneous steel | ||
| Location | Thickness | Angle from vertical |
| Gun shield | 3.5" 8.9cm |
0° |
| Front | 3.0" 7.6cm |
0° |
| Sides | 2.5" 6.4cm |
0° to 13° |
| Rear | 2.5" 6.4cm |
0° |
| Top | 1.0" 2.5cm |
90° |
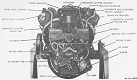
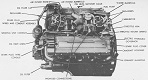
| T23: Automotive | |||||
| Engine | Ford GAN; 8 cylinder, 4 cycle, 60° vee gasoline | ||||
| Horsepower | Net: 450@2,600rpm Gross: 500@2,600rpm |
Torque | Net: 950 ft-lb@2,200rpm Gross: 1040 ft-lb@2,200rpm |
Fuel capacity | 179gal 678L |
| Transmission | Electric drive | ||||
| Steering | Electric, steering levers | ||||
| Brakes | Electric and mechanical Bendix | ||||
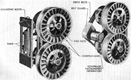
| T23: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Vertical volute spring | 3 bogies/track; 2 wheels/bogie |
1 at rear of each bogie |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | 13-tooth rear drive | Adjustable at front of track | None |
| T23: Track | |||||||
| T48 | |||||||
| Outside guide, double pin, chevron, rubber | |||||||
| Width | 16.56" 42.06cm |
Pitch | 6" 15cm |
Shoes/track | 79 | Ground contact length | 147" 373cm |
| T51 | |||||||
| Outside guide, double pin, smooth, rubber | |||||||
| Width | 16.56" 42.06cm |
Pitch | 6" 15cm |
Shoes/track | 79 | Ground contact length | 147" 373cm |
| T23: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 35mph 56kph |
Max trench | 90" 230cm |
| Max grade | 60% | Max vertical obstacle | 24" 61cm |
| Min turning diameter | Pivot | Max fording depth | 48" 120cm |
| Cruising range | ~100mi, roads ~160km, roads |
||
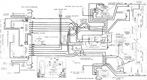
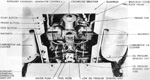
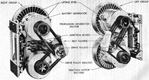
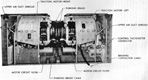
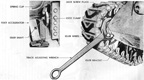
The T23 was one of the T20 series of medium tanks designed to replace the M4 Sherman, ultimately culminating in the M26 Pershing. The T23 pilots were the first of the T20 series tanks to be completed, and the only to be produced serially besides the M26. The T23's electric drive mechanism was a novel way to move a tank, with a similar system having been previously tested in the heavy tank T1E1 (sometimes referred to as M6A2), and worked by having the GAN engine power an electric generator which in turn drove two traction motors which were connected to the tank's final drives. This allowed the engine to operate at its most efficient speed at all times since there was no direct connection between the engine and tracks, and also provided an infinitely variable turning radius. The vehicle could be driven from the turret or even outside by using controllers connected to the tank via cables. T23 was fitted with the same VVS suspension as the M4 Sherman, and the two tanks were further interconnected when the T23's turret was adopted for use on the 76mm gun M4s. Wet ammunition stowage was to be used: six wet ammunition racks were installed, three behind the driver and three behind the assistant driver. A 26-round ammunition rack on each side of the vehicle contained two removable water tanks, one on the sponson side and one in the forward compartment. The tanks were connected by tubes and held a total of ~7gal (~26L). In addition, four rounds apiece were stowed in containers attached to the vehicle wall directly above the 26-round racks that held ~2gal (~8L) of liquid. Two rounds apiece were stowed in containers on the wall directly above the 4-round racks. These held ~1.5gal (~6.8L) of fluid.
Although it was proposed to standardize T23 as the medium tank M27 once it had been fitted with torsion bar suspension (making it T23E3), it was not adopted due to maintenance problems and concerns over training of maintenance personnel to deal with the electric drive system. However, T23 eventually lived on as the M26, which had been designated T26E3. The T26 was a more heavily armored version of the T25, which was essentially a 90mm gun-armed T23.






















































