



















































| M56: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | December 1957 | Total acceptances | 160 |
| Manufacturer | Cadillac Motor Car Division of General Motors Corp. | Crew |
|
| M56: Dimensions | |||
| Combat weight | 15,750lbs 7,144kg |
Height over blast shield | 78.9" 200cm |
| Length without gun | 179.4" 455.7cm |
Gun overhang forward | 50.4" 128cm |
| Width over fenders | 101.3" 257.3cm |
Tread | 78.0" 198cm |
| Ground clearance | 12.8" 32.5cm |
Fire height | 66.0" 170cm |
| Ground pressure, zero penetration | 4.2psi .29kg/cm² |
||
| M56: Armament | ||||
| Type | Mount | Ammunition | Traverse | Elevation |
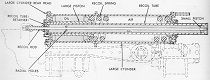
| 90mm Gun M54 | M88 on hull center | 29 rounds | 60° (30° left and right manual) |
+15° to -10° (manual) |
| Aiming equipment | ||||
| Telescope M91D for gunner | ||||
| M56: Armor |
| None |
| M56: Automotive | |||||
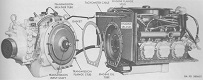
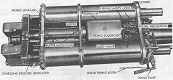
| Engine | Continental AOI-402-5; 6 cylinder, 4 cycle, opposed, fuel injected gasoline | ||||
| Horsepower | Net: 165@3,000rpm Gross: 200@3,000rpm |
Torque | Net: 325 ft-lb@2,200rpm Gross: 347 ft-lb@2,800 |
Fuel capacity | 55gal 210L |
| Transmission | Allison CD-150-4, 2 ranges forward, 1 reverse | ||||
| Steering | Mechanical, steering wheel | ||||
| Brakes | Multiple disc | ||||
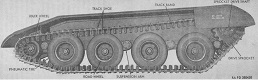
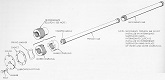
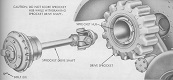
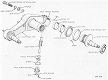
| M56: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Torsion tube over bar at wheels 1 and 4, torsion bar at wheels 2 and 3 | 4 individually sprung/track with pneumatic tires | Flat track |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | 15-tooth front drive | Compensating at rear of track | On first and last road wheels/track |
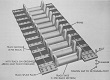
| M56: Track | |||||||
| T103 | |||||||
| Outside guide band type | |||||||
| Width | 20" 51cm |
Pitch | 44” long sections; 4” cross bar pitch 110cm long sections; 10cm crossbar pitch |
Shoes/track | 8 sections/track; 88 cross bars/track |
Ground contact length | 94" 240cm |
| M56: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 28mph 45kph |
Max trench | 48" 120cm |
| Max grade | 60% | Max vertical obstacle | 30" 76cm |
| Min turning diameter | Pivot | Max fording depth | 42" 110cm |
| Cruising range | ~140mi, roads ~230km, roads |
||
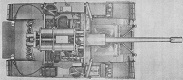
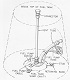
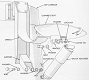
The M56, also known as SPAT for Self-Propelled AntiTank, or more colloquially as the Scorpion, was designed as an airborne antitank gun. The 90mm gun M54 was ballistically identical to and used the same ammunition as the M36 90mm gun in the M47 tank, and it was fitted with a blast deflector. The M56 was unarmored, and consisted of little more than a gun mounted on a tracked riveted-aluminum alloy carrier. There was a small blast shield fitted to the weapon, and this had a windscreen in the left side for the driver to look through. Creature comforts were nonexistent as the vehicle was completely open. The commander sat on top of the radio, and the loader's seat was on top of the right fender stowage box, leaving the gunner and driver as the only crewmen "in" the vehicle. Recommended tire pressure was 75psi (5.2bar), but the tires on the M56 could run flat up to 15mi (24km) at up to 15mph (24kph). The ammunition rack was located in the lower rear hull, and the loader was provided with a folding platform from which to feed the gun.































































