

































| M55: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | August 1952 | ||
| Manufacturer | Pacific Car and Foundry Co. | Crew |
|
| M55: Dimensions | |||
| Combat weight | ~98,000lbs ~44.000kg |
Height over AAMG mount | 136.6" 347.0cm |
| Length without howitzer | 311.4" 791.0cm |
Howitzer overhang forward in travel position | 0" |
| Width over fenders | 141.0" 358.1cm |
Tread | 110.0" 279.4cm |
| Ground clearance | 18.5" 47.0cm |
Fire height | ~95" ~240cm |
| Turret ring diameter | 59.5" 151cm |
Ground pressure, zero penetration | 11.6psi .817kg/cm² |
| M55: Armament | ||||||
| Type | Mount | Ammunition | Traverse | Max traverse rate | Elevation | Max elevation rate |
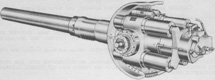
| 8" Howitzer M47 | M86 in turret | 10 rounds | 60° (30° left or right; manual and hydraulic) |
10°/sec | +65° to -5° (manual and hydraulic) |
7.5°/sec |
| .50cal M2HB MG | Flexible in cupola AA mount | 900 rounds | 360° (manual) |
-- | Manual | -- |
| Aiming equipment | ||||||
| Panoramic telescope M100 and telescope M99 for gunner | ||||||
| M55: Armor | ||
| Assembly | ||
| Welding | ||
| Hull | ||
| Rolled homogeneous steel | ||
| Location | Thickness | Angle from vertical |
| Upper front | 1.0" 2.5cm |
10° |
| Lower front | 1.0" 2.5cm |
59° |
| Sides | 0.5" 1.3cm |
0° |
| Rear | 0.5" 1.3cm |
22° |
| Top | 0.5" 1.3cm |
90° |
| Floor | 0.5" 1.3cm |
90° |
| Turret | ||
| Rolled homogeneous steel | ||
| Location | Thickness | Angle from vertical |
| Front | 0.5" 1.3cm |
20° |
| Sides | 0.5" 1.3cm |
0° |
| Rear | 0.5" 1.3cm |
0° |
| Top | 0.5" 1.3cm |
90° |
| M55: Automotive | |||||
| Engine | Continental AV-1790-5B or -7B; 12 cylinder, 4 cycle, 90° vee gasoline | ||||
| Horsepower | Net: 704@2,800rpm Gross: 810@2,800rpm |
Torque | Net: 1,440 ft-lb@2,000rpm Gross: 1,610@2,200rpm |
Fuel capacity | 380gal 1,440L |
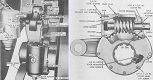
| Transmission | General Motors CD-850-4 or -4B, 2 ranges forward, 1 reverse | ||||
| Steering | Mechanical, wobble stick | ||||
| Brakes | Multiple disc | ||||
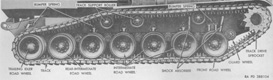
| M55: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Torsion bar | 7 independently sprung dual/track | 3 dual/track |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | 13-tooth front drive | Dual trailing adjustable at rear of each track | On first 2 road wheels/track |
| M55: Track | |||||||
| T80E6 | |||||||
| Center guide, double pin, rubber backed steel | |||||||
| Width | 23" 58cm |
Pitch | 6" 15cm |
Shoes/track | Left side: 89 Right side: 90 |
Ground contact length | 184" 467cm |
| T84E1 | |||||||
| Center guide, double pin, rubber chevron | |||||||
| Width | 23" 58cm |
Pitch | 6" 15cm |
Shoes/track | Left side: 89 Right side: 90 |
Ground contact length | 184" 467cm |
| M55: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 35mph sustained 56kph sustained |
Max trench | 96" 240cm |
| Max grade | 60% | Max vertical obstacle | 42" 110cm |
| Min turning diameter | Pivot | Max fording depth | 60" 150cm |
| Cruising range | ~150mi ~240km |
||
The M55 was based on components of the M46 and M47 Patton tanks. The engine and transmission were at the front, and the large turret was at the rear. The entire crew was housed in the turret, with the driver stationed at the front left of the turret. Improvements in the medium tank series were grafted onto the M55 as they appeared; the AV-1790-7B engine and CD-850-4B transmission were introduced, and a steering wheel replaced the wobble stick control. The 155mm self-propelled gun M53 utilized the same chassis, and the M86 mount could accept either ordnance. Ammunition stowage racks were interchangeable between the two vehicles as well. The Army converted all of its M53s to M55s starting in 1956, but the Marine Corps continued to use the M53.










































